LinkedIn is the haven for B2B digital marketing and professional networking alike because it comes equipped with extensive, specific professional demographic information that far exceeds any other social media channel, and in terms of targeting, it can be your number one resource if used properly.
So, if you’re looking to create a killer LinkedIn ad campaign, this article shows you how to use LinkedIn ads targeting as a complete guide to get you on the road to smashing. We’ll also go beyond the best practices used by our LinkedIn Ads agency.

Case Study: How We Helped a Security Analytics Software Company Generate 42% More SQLs Using LinkedIn Ads
1 – What are LinkedIn’s Audience Targeting Options?
A big part of campaign success on LinkedIn comes down to good targeting, so with that in mind, let’s look at your options for audience targeting and how to utilise them for a successful LinkedIn ad campaign.
First things first, though: it is crucial before beginning the audience building process, and your campaign itself, that you finely pinpoint the exact objective of the campaign. Be as specific as possible to ensure your efforts will be met with the most relevant viewers.

Next, choose your type of ad. You have three options here: InMail, text ads, or sponsored content. Once you’ve done that, this will further aid your targeting specifics. Audience targeting is based on “matched audiences” or “audience attributes” – or both. More on this later…
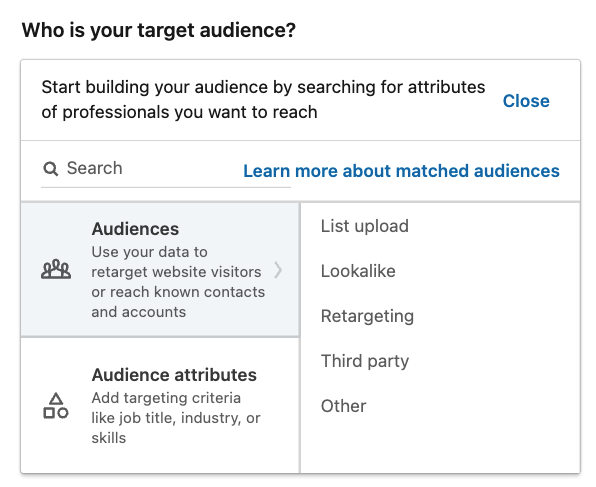
2 – A Guide to Audience Targeting on LinkedIn
2.1 – Demographic Targeting
Naturally, a key targeting option on LinkedIn is demographic targeting. LinkedIn is perfect for this, because its professional demographic user information is vast and precise. You can start building your audience by searching for the attributes relevant to the campaign’s focus.
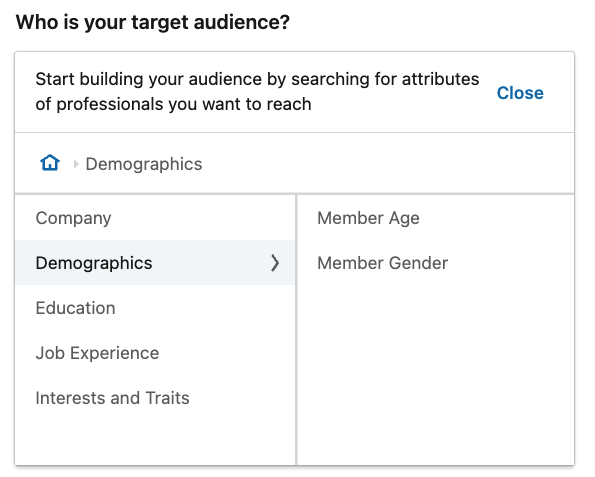
To start with demographic user data search, you have “Member Age” and “Member Gender”. LinkedIn’s Age Categories are broken down into the following: 18 to 24, 25 to 34, 35 to 54, and 55+.
– Member Age: An estimation of how old a member is based on their profile information.
– Member Gender: Determination of whether a member is female or male is inferred, based on their profile information.
2.2 – Company Targeting
For ad campaigns, targeting whole companies can be beneficial for making sure your B2B marketing campaign is reaching the right people.

You can start building your company-based audience with the following:
– Company Connections. This will help you reach 1st-degree connections of employees at your chosen companies. Please note: this method is only productive if the companies have over 500 employees.
– Company Followers. This will help you reach your own company page’s current followers.
– Company Name. This allows you to target certain individuals at your chosen companies, such as key decision makers/C-Level employees.
– Company Industry. This will help you target your industry as a whole, meaning considerable outreach and efficiency.
– Company Size. This allows you to be specific about the companies you target based on their sizes. Please note: this method only works if a company has listed the employee number bracket on their page. The brackets go from 1 to 10 employees, 11 to 50, and then gradually increase. It is also possible to target self-employed users/freelancers too, if your campaign calls for that type of audience.
2.3 – Jobs Targeting
Jobs targeting allows you to be more specific about your target audience in terms of their roles. Here are your options:

– Job Functions. Naturally, this option homes in on member groupings per their job function.
– Job Seniority. This allows you to target a company’s users at their specific levels within the business.
– Job Title. Titles will be grouped into standardised titles by LinkedIn’s algorithm for a more specific level of targeting.
– Member Skills. If your campaign needs to target a generalised skill (marketing, outreach, copywriting, customer service, and so on), LinkedIn’s algorithm will take into account a user’s skills (both listed and endorsed).
– Years of Experience. This allows you to home in on users with specific levels of experience within their industry, which is beneficial if expertise is required of your audience. Please note: overlapping positions do not count as two separate jobs.
2.4 – Education Targeting
This is more specific than a user’s high school credentials. This area predominantly focuses on further education, what type of award was achieved, and what score. This also allows for targeting based on general and inferred skills, which will expand your audience while still keeping it relevant. Here is a breakdown of this targeting method:
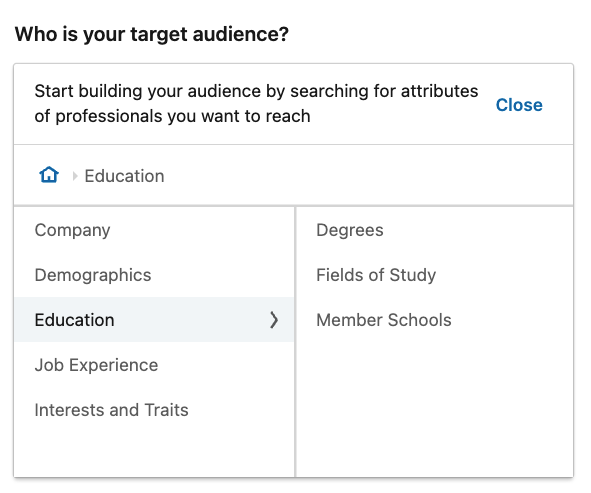
– Fields of Study: The major or area of study within a member’s degree. Standardised from member-entered degrees.
– Member Schools: The school, college, university, or other learning institution where a LinkedIn member completed a certification.
– Degrees: Recognized certifications granted by a university, college or other learning institution.
2.5 – Interest Targeting
Depending on the subject/purpose of your LinkedIn ad campaign, a user’s listed interests can be a key indicator of whether they are an ideal audience target. Again, LinkedIn is encouraging of its users utilising the fields of information on their profiles in order for its algorithm to do its job in seeking appropriate audiences for appropriate campaigns; not to mention for recruitment purposes.
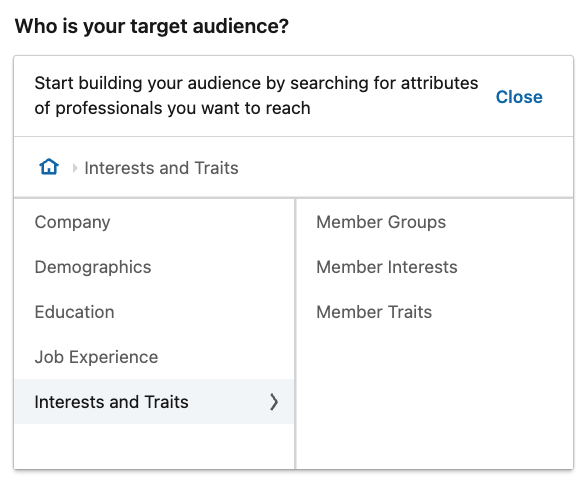
These are the two LinkedIn interest targeting options:
– LinkedIn Member Groups targeting. These groups are there for users to network with likeminded individuals/members of the same professional organisations, past or present.
– LinkedIn Member Interests targeting. This is a vast catalogue of interests users partake in outside of work. This can be anything from sport to charity fundraising and environmental causes, to name but a few.
Case Study: How We Helped Kodo Survey to Generate 167% More Leads in 3 Months Using LinkedIn Ads
2.6 – Buyer Group Targeting
LinkedIn’s Buyer Group Targeting is a new feature aimed at reaching decision-makers within predefined groups.
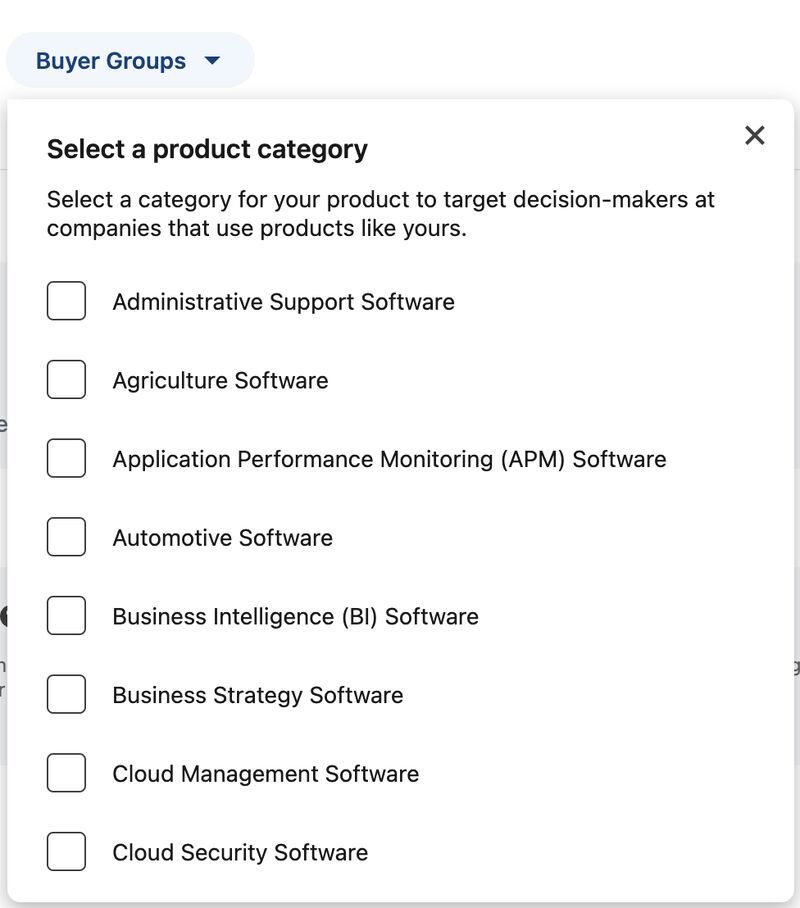
While it has potential, it comes with limitations that may impact its effectiveness. Here’s how it works
– Options: Similar to Product Interests, you can choose one Buyer Group per campaign, with a larger audience size.
– Exclusions: Limited to Seniority, Company Industry, and Company Lists, restricting audience refinement.
– Insights: No audience insights are available, leaving the composition unclear.
What the Audience Looks Like:
- A mix of seniority levels, with most having 12+ years of experience.
- Relevant job functions and industries tied to the selected Buyer Group.
- Balanced company sizes, avoiding oversaturation by large enterprises.
Buyer Group Targeting works best as an experiment to identify high-performing segments for future campaigns.
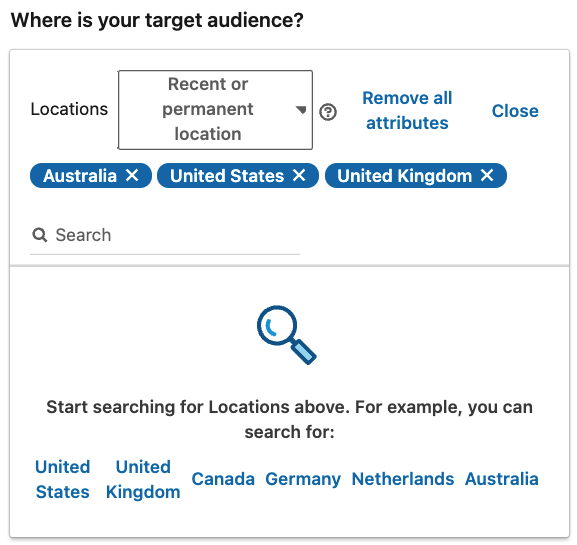
2.7 – Locations Targeting
This is rather self-explanatory, but LinkedIn will enable targeting based on a specific location/s as outlined on a user’s page or IP address (this is for regular travellers). Location targeting isn’t generic, meaning LinkedIn will allow you to be specific about where you want to focus on, and will also allow you to exclude any areas not relevant to your campaign.
2.8 – Audience Network and Expansion Targeting
The audience expansion targeting feature works as an extension of your outlined target audience by targeting other users with similar attributes to your listed current audience. This can work based on the user’s media habits (their impressions and engagement with other content on LinkedIn). Again, you are in a position to be picky and exclude any attributes you deem irrelevant.

The LinkedIn Audience Network is a feature that allows you to extend the reach of your Sponsored Content campaigns by delivering your ads beyond the LinkedIn feed to members on third-party apps and sites. The goal here is simple: increased audience expansion; specifically to those who may not be a member of LinkedIn. By using Audience Network, you could potentially reach millions of professionals on multiple other touchpoints – just by enabling this option whilst publishing your ad campaigns on LinkedIn.
2.9 – Matched Audience Targeting
This focuses on audiences that have already engaged with your brand in the past (and not just on LinkedIn; this data can be collected from your website’s cookies, and whether the user is on your company’s email list, etc.) This is effectively audience retargeting. Other factors that can be utilised with LinkedIn match audiences include CVS uploading and CRM (Customer Relationship Management) system integration.

2.10 – Predictive Audiences
This is one of LinkedIn’s more recent targeting functions. This option works for companies who use a CRM system and allows them to upload an email list from that system, with LinkedIn matching its details against its own database. This can save a lot of time in your targeting movements.
2.11 -Bing Search Data
Bing Search Data works well in conjunction with Interest Targeting, as when the two are combined it gathers more relevant information to create an ideal audience (who use the search engine, Bing, of course). While Bing isn’t as powerful as Google, it is still a popular search engine, so this option shouldn’t be forsaken on account of Bing being less popular than Google.
3 – LinkedIn Ads Targeting: Best Practices
When you’re compiling your target audience on LinkedIn, here are some key focuses and practices you should implement to harness success:
3.1 – Audience Size
Before you start building your LinkedIn ads campaign, it is wise to ask yourself about what size your audience should be. If you haven’t a clue, allow us to help!
The minimum LinkedIn audience size for a campaign should be no less than 300 members, although it is recommended by LinkedIn themselves to aim for a minimum of 300,000 audience members for a sponsored (paid) content, and anywhere between 60,000 and 400,000 for a text ad campaign.
Naturally, this can depend entirely on your brand, industry, and the purpose of your campaign. If your industry or campaign is somewhat niche, this may mean your target audience size might be on a smaller scale.
However, that said – aiming for anywhere in between 30,000 – 100,000 is usually a winning target for any given campaign.
3.2 – Location
Whenever you start creating a LinkedIn ads campaign, you will immediately be asked to identify the location of your target audience – and you will be expected to put something in, as this field is mandatory (and is the only mandatory field throughout the process). If you’re unsure where to begin, so to speak, here are your two options:
– Narrow Targeting, meaning specific cities or metropolitan areas.
– Broad Targeting, meaning states or country-wide locations.
A good place to start is choosing your location based on where your company’s headquarters are, or the prime location it focuses on servicing. Obviously, this may not be the case depending on the type of industry you’re in, and the purpose behind your campaign.
If your company caters to international clients, this can make targeting a little more complicated as you’ll need to set up separate campaigns based on each region. Now is an important time to mention that the success of your campaign can vary from location/country to location/country. This doesn’t necessarily mean your ad campaign is flawed or failing. This could just be down to various factors, such as that location’s economic climate, trading laws, and so on.
You can also target people of a “permanent location” (users who permanently live/work in one location only), or “recent location” (somewhere they may have visited for business purposes/users who travel for business on a regular basis).
Both have their uses, depending on your ad campaign’s objectives, but generally speaking, opting for permanent location will likely secure more leads.
LinkedIn targeting best practices are critical for improving your performance.
4 – Types of Ads for Targeting your Advertising on LinkedIn
With LinkedIn, there are more than one type of ad options for you to choose for your campaign, and each type has its benefits for different types of campaigns based on the target audience and the brand’s objectives. At present, the types of ads for targeting your advertising on LinkedIn are as follows:
– SPONSORED CONTENT ADS. This option can be ideal if the key focus of your campaign is lead generation. This purpose behind it is to encourage a target audience to engage with a brand in the early stages of their buying journey. A sponsored content ad will be placed in front of LinkedIn users who are likely to convert.
– SPONSORED INMAIL ADS. Please note: this option is only available to LinkedIn Premium users, with the benefit being these ads will land directly into a target user’s LinkedIn inbox. It also provides more opportunity to personalise your ad than a standard sponsored content ad – and the ad will land in their inbox while they’re logged onto their LinkedIn account, meaning a higher likelihood of the ad being viewed.
– TEXT ADS. Text ads are designed for marketers on a lower budget, and can be a great tool to use if your campaign’s focus is traffic-driving. LinkedIn text ads can appear in four different format options: tall, long, square, or horizontal.
This campaign autonomy allows you to choose the right type of ad for the right type of audience, based on your campaign’s key objective. LinkedIn’s KPIs also allow you to monitor the success of your campaign in real-time, so as to make any necessary amendments to you content, if need be.
Conclusion
So, now that we’ve broken down the fundamentals of accurately targeting your LinkedIn ad campaign, this should get you on the road to success with reaching the right audience to meet your marketing objectives.
LinkedIn is a brilliant and extensive platform for being as specific as possibly when it comes to reaching a precise group of users to ensure your campaign is successful, so taking the time to be sure of your campaign’s goals, as well as the right targeting options per your campaign, will help you to harness the information you need to directly target the most conversion-likely leads.
If you’d like to learn more about how we help B2B SaaS and Tech companies grow their MRR through LinkedIn advertising, contact us online or send us an email today at info@getuplead.com to speak with someone on our team.
You might also be interested:
- Linkedin Ad Campaign Objectives: How to Choose the Right One
- LinkedIn Retargeting: How It Works & How to Set It Up
- How to add a User to LinkedIn Campaign Manager?
- A Complete Guide to LinkedIn Tracking for Beginners
- Linkedin Bidding Strategies: The Complete Guide
- LinkedIn Ad Optimization: Tips and Best Practices


